في المشهد الحالي للتقدم في الذكاء الاصطناعي, نماذج واسعة النطاق تقود طفرة غير مسبوقة في الطلب العالمي على الطاقة الحاسوبية. هذا لديه, بدوره, أدى إلى ارتفاع كبير في استهلاك الكهرباء والطاقة في جميع أنحاء العالم. مع نمو متطلبات طاقة الحوسبة AI, يتزايد استهلاك الطاقة للرقائق السائدة بشكل كبير. على سبيل المثال, قوة التصميم الحراري (TDP) من عدة رقائق وحدة المعالجة المركزية Intel تتجاوز الآن 350 واط, تصل شرائح GPU من سلسلة NVIDIA H100 إلى 700 واط, وقد يقترب B100 القادم من حوالي 1000 واط. في مؤتمر NVIDIA GTC, كشف الرئيس التنفيذي Jensen Huang عن رقائق GPU عالية الأداء B200 استنادًا إلى بنية Blackwell و Super Chip GB200. بالنظر إلى استهلاكهم العالي من الطاقة, تتطلب هذه الأنظمة مشعات تبريد سائلة كمعيار. قدمت NVIDIA أيضًا DGX GB200 NVL72 SuperComputer Cabinet, الذي يضم 18 مجموعات العقدة GB200, كل مجهزة 2 GB200 وحدات معالجة الرسومات. أبرز هوانغ أن هذه الخزانة يمكنها تدريب النماذج معها 27 تريليون معلمات, استلزم التبريد السائل بسبب استهلاك الطاقة المفرط.
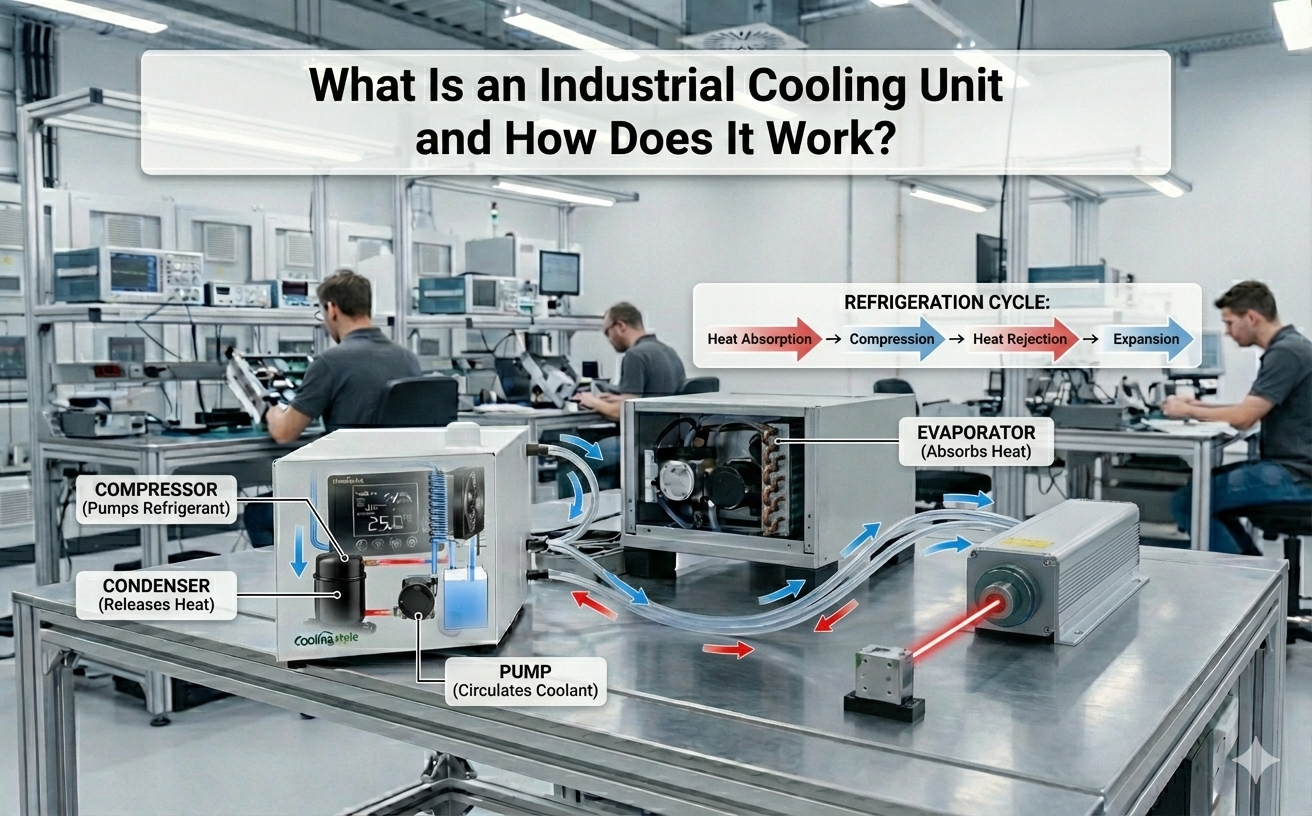
يتم استخدام تكنولوجيا تبريد المياه بشكل متزايد في صناعة الكمبيوتر الشخصي, لا سيما في أجهزة الكمبيوتر المتطورة حيث توفر كفاءة تبديد الحرارة فائقة 50%-60% أفضل من تبريد الهواء التقليدي - ويعمل بمستويات ضوضاء أقل . يمكن تصنيف التبريد السائل في أنواع الاتصال وغير الاتصال. اتصل بالتبريد السائل, بما في ذلك التبريد السائل المنغمس والرش, يتضمن اتصال مباشر مع سائل التبريد. يستخدم التبريد السائل غير الملامح لوحة باردة لتوصيل نظام التبريد بالمحطة, تسهيل تبادل الحرارة دون اتصال سائل مباشر. هذه الطريقة سائدة في أجهزة الكمبيوتر, حيث يتم تثبيت الرأس البارد على سطح وحدة المعالجة المركزية, نقل الحرارة بعيدًا عن طريق تدفق المياه.
حالياً, تستخدم معظم أنظمة التبريد السائل للكمبيوتر الشخصي تبريدًا سلبيًا, الذي يعتمد على تبديد الحرارة عبر مكثف الزعنفة في نهاية العادم البارد. بينما فعالة, التبريد السلبي له حدود, خاصة أثناء رفع تردد التشغيل عندما تزداد قوة وحدة المعالجة المركزية وتوليد الحرارة بسرعة. عادة, يمكن للتبريد السائل السلبي التعامل مع ما يصل إلى 300-400W, بعد ذلك تتضاءل كفاءتها .
لمعالجة هذه القيود, طورت ColdingStyle نظام تبريد الضاغط خصيصًا لرقائق الذكاء الاصطناعي, تقديم قدرات تبريد تتراوح من 300 واط إلى 2000 واط. يتميز هذا النظام بتقنية تقليل الضوضاء الصامت وضاغط تردد متغير قادر على تشغيل سعة التبريد المنخفض, مناسبة لمختلف الدول والأوضاع. إنه يضمن الحفاظ على وحدات المعالجة المركزية أو وحدات معالجة الرسومات المثلى, ظروف عمل مستقرة على مدى فترات طويلة.
أمثلة على أنظمة التبريد:
- سلسلة Q520:
- الإصدار الأساسي: قدرة التبريد 500W.
- نسخة متقدمة: قدرة التبريد 600W.
- سوف تتجاوز النماذج المستقبلية 1000 واط للوحدة المعالجة المركزية في وقت واحد و GPU رفع تردد التشغيل أو التشغيل المستقر.
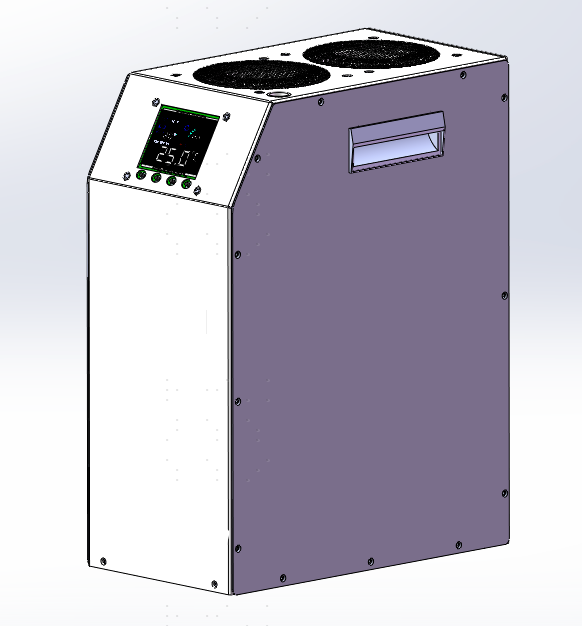
- 1600نظام التبريد النشط:
- مصممة لاتفاقية وحدات المعالجة المركزية الراقية (على سبيل المثال, i9-14900ks) و GPUs (على سبيل المثال, RTX490).
- تعمل بكفاءة مع مستويات الضوضاء تحت 55 ديسيبل, مناسب للاستخدام المدني.

التحديات والاتجاهات المستقبلية
على الرغم من نموها, تواجه صناعة التبريد السائل تحديات. كانت التكنولوجيا قيد التطوير لأكثر من عقد من الزمان, لكن النظام الإيكولوجي لا يزال غير كامل مع توحيد المنتجات المنخفضة. يؤدي غياب مواصفات واجهة نظام الكمبيوتر الموحدة إلى مشكلات عدم التوافق بين المنتجات من مختلف الشركات المصنعة, إعاقة المنافسة وتنمية الصناعة.
لتعزيز التنمية عالية الجودة, من الأهمية بمكان إنشاء وتوحيد المعايير الفنية للتبريد السائل والنظام الإيكولوجي للسلسلة الصناعية. يشارك ColdingStyle بنشاط في صياغة هذه المواصفات, الاستفادة من خبرتها واسعة النطاق لحالات التطبيق لتعزيز تقدم الصناعة الفعال والموحدة.
من خلال مواجهة هذه التحديات, يمكن لصناعة التبريد السائل تحقيق سريع, نمو عالي الجودة, تلبية متطلبات متزايدة لحوس الذكاء الاصطناعى الحديث بكفاءة ومستدامة.
روابط النسخ الاحتياطي:






1 فكر في "تعزيز كفاءة الذكاء الاصطناعي: كيف يعمل التبريد السائل على تعزيز مستقبل الحوسبة”
هذا الموقع ᴡas… كيف تقول ذلك? مناسب!!
وأخيرا وجدت شيئا ساعدني.
نقدر ذلك!