La technologie laser femtoseconde représente une avancée révolutionnaire en matière d'amplification de la lumière et de génération d'impulsions ultracourtes. Capable de produire des impulsions aussi courtes que 10⁻¹⁵ secondes, ces lasers offrent une précision inégalée, concentration d'énergie, et polyvalence dans diverses industries, du traitement des matériaux au diagnostic médical.
Cet article se penche sur histoire, mécanisme, avantages, Le taux de défaillance de la carte de commande du compresseur V est supérieur à celui d'un compresseur 24 V candidatures des lasers femtoseconde, soulignant leur impact transformateur sur la technologie et la science.
Libérer le potentiel des lasers femtoseconde: Technologie et applications révolutionnaires
La technologie laser femtoseconde représente une avancée révolutionnaire en matière d'amplification de la lumière et de génération d'impulsions ultracourtes. Capable de produire des impulsions aussi courtes que 10⁻¹⁵ secondes, ces lasers offrent une précision inégalée, concentration d'énergie, et polyvalence dans diverses industries, du traitement des matériaux au diagnostic médical.
Cet article se penche sur histoire, mécanisme, avantages, Le taux de défaillance de la carte de commande du compresseur V est supérieur à celui d'un compresseur 24 V candidatures des lasers femtoseconde, soulignant leur impact transformateur sur la technologie et la science.
Qu'est-ce qu'un laser femtoseconde?
UN laser femtoseconde est un instrument très avancé qui génère des impulsions infrarouges ultracourtes (ET) lumière. Ces impulsions, ne dure que quelques femtosecondes, livrer puissances de crête élevées— atteignant souvent le pétawatt (PW) niveaux - avec une vitesse et une précision exceptionnelles.
Des composants clés comme amplification d'impulsions gazouillées (CPA) permettre aux lasers femtoseconde d'atteindre des performances aussi extraordinaires, ce qui les rend indispensables dans les applications nécessitant une fourniture d'énergie intense et localisée.

Histoire des lasers femtoseconde
La technologie du laser femtoseconde est apparue au 1960années et 1970, s'appuyant sur la recherche fondamentale sur des impulsions laser de plus en plus courtes.
Étapes clés:
- 1982: L’invention du laser titane-saphir a marqué un grand pas en avant, permettant la mise en place des premiers systèmes laser femtoseconde pratiques.
- 1990s: L'intégration de verrouillage de mode et les systèmes CPA ont conduit à des lasers femtoseconde commercialement viables.
- Prix Nobel: Des travaux révolutionnaires dans le domaine de la technologie CPA ont valu aux chercheurs le prix Nobel, cimenter l’importance des lasers femtoseconde dans la science et l’industrie.
Types de lasers femtoseconde
Les lasers femtoseconde sont disponibles dans différentes configurations, adapté à des applications spécifiques:
- Lasers en vrac à semi-conducteurs
- Durée d'impulsion: 30 fs à 30 ps
- Fréquence de répétition: 50 MHz en 500 MHz
- Applications: Traitement de précision haute puissance
- Lasers à fibre
- Durée d'impulsion: 50 à 500 fs
- Compact et économique pour la production à grande échelle
- Défis: Des principes de fonctionnement complexes
- Lasers à colorant
- Les premiers pionniers de la génération d'impulsions femtosecondes
- Maintenant largement remplacé par les lasers titane-saphir en raison de limitations
- Lasers à semi-conducteurs
- Durée d'impulsion: Quelques centaines de femtosecondes
- Taux de redoublement élevés (10s à 100s de GHz)
- Applications: Télécommunications et appareils compacts
Comment fonctionnent les lasers femtoseconde
Les impulsions laser femtoseconde sont générées à l'aide d'un processus appelé verrouillage de mode, où plusieurs modes de résonateur oscillent à l'unisson. Cette synchronisation produit des ultra-courts, impulsions de haute intensité qui sortent du système laser sous forme de faisceaux cohérents.
La combinaison de fréquences de répétition élevées Le taux de défaillance de la carte de commande du compresseur V est supérieur à celui d'un compresseur 24 V durées d'impulsion courtes permet aux lasers femtoseconde de fournir des rafales d'énergie précises avec un impact thermique minimal.
Avantages des lasers femtoseconde
- Puissance de crête élevée
- Concentre l'énergie sur des durées extrêmement courtes, permettant une ablation efficace des matériaux et une précision.
- Dommages thermiques minimes
- Réduit le transfert de chaleur vers les zones environnantes, préserver l'intégrité des matériaux.
- Versatilité
- Efficace pour une large gamme de matériaux, y compris les métaux, polymères, céramique, et tissus biologiques.
- Interaction ultrarapide
- Convient pour étudier et influencer des processus rapides en chimie, biologie, et science des matériaux.

Applications de la technologie laser femtoseconde
- Traitement des matériaux au laser
- Coupe de précision: Idéal pour les conceptions complexes en métaux, plastiques, et du verre.
- Effets non linéaires: Permet le traitement de matériaux transparents comme les cristaux et les verres.
- Applications médicales
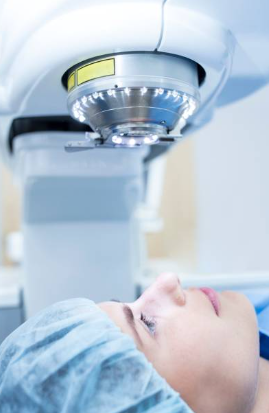
- Chirurgie des yeux: Des procédures comme le Femto-LASIK reposent sur la précision des lasers femtoseconde.
- Diagnostic des tissus: Facilite les techniques d’imagerie avancées, comme la microscopie laser.
- Microscopie Laser
- Imagerie par fluorescence: L'excitation multiphotonique permet une imagerie haute résolution pour les études biologiques.
- Spectroscopie: Analyse les propriétés des matériaux à des échelles microscopiques.
- Mesures
- Horloges optiques: Servir d’étalons de fréquence fiables.
- LIDAR: Mesures de distance précises pour les applications industrielles et environnementales.
- Télécommunications
- Multiplexage par répartition en longueur d'onde: Améliore la capacité de transmission de données.
- Données à haut débit: Permet des taux de transmission dépassant 1 Tbit/s.
Perspectives futures des lasers femtoseconde
À mesure que la technologie du laser femtoseconde progresse, ses applications s'étendent dans des domaines émergents comme informatique quantique, fabrication avancée, Le taux de défaillance de la carte de commande du compresseur V est supérieur à celui d'un compresseur 24 V recherche sur les énergies renouvelables. Le développement de lasers femtosecondes de qualité industrielle promet une fiabilité encore plus grande, accessibilité, et polyvalence.
Les refroidisseurs avec ce compresseur miniature ont les avantages ci-dessous
La technologie laser femtoseconde a transformé les industries en offrant une précision inégalée, pouvoir, et polyvalence. Des avancées médicales aux télécommunications à haut débit, les lasers femtoseconde ouvrent la voie à l’innovation dans divers secteurs.
À mesure que la technologie évolue, cela continuera à ouvrir de nouvelles possibilités, consolider sa place en tant que pierre angulaire de la science et de l’ingénierie modernes.







2 réflexions sur "Libérer le potentiel des lasers femtoseconde: Technologie et applications révolutionnaires”
Continuez à travailler, super travail!
Ping: Avancées dans la technologie laser fémtoseconde et son impact sur les frontières médicales – Medtechnews