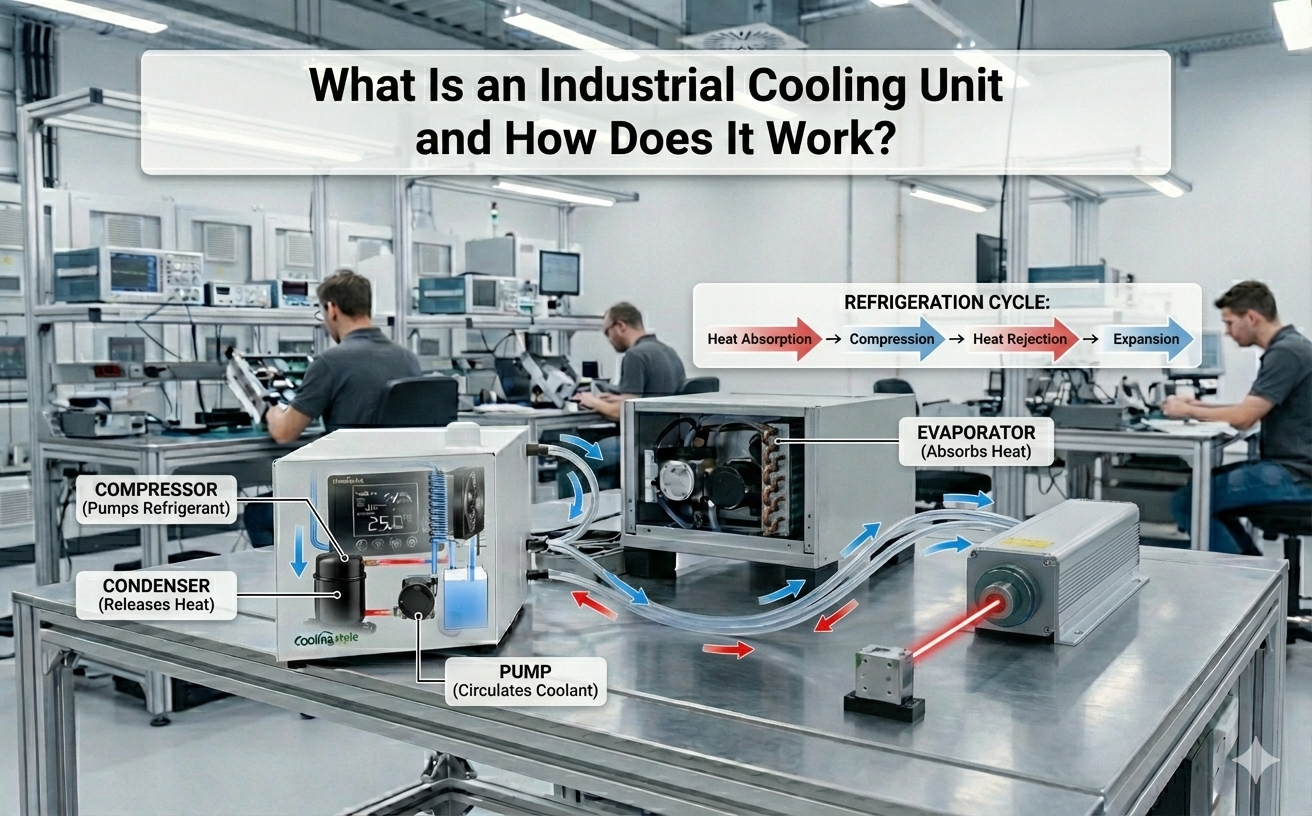
Lasers generate significant heat during operation, making temperature control critical to their performance. Chiller systems are integral to maintaining the efficiency and longevity of lasers, whether in industrial, medical, or everyday applications. This article delves into the essentials of laser cooling, its importance, and the benefits of using chillers to ensure precision and reliability.
What Are Lasers Used For?
The term “laser” stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, a technology that has permeated various industries, including:
- Retail: Barcodes have been ubiquitous since 1952.
- Manufacturing: Welding, printing, and marking rely heavily on lasers.
- Military and Telecommunications: Lasers are pivotal for advanced applications.
- Healthcare: Widely used in medical procedures and diagnostics.
The Role of Chillers in Laser Cooling
Preventing Overheating:
Chillers efficiently dissipate heat from lasers, protecting sensitive components and maintaining consistent performance. Vapor compression water chillers are commonly employed to regulate temperatures below ambient levels in laser systems.
Prolonging Equipment Lifespan:
Stable temperatures enhance the operational life of lasers, ensuring precision and reliability across their lifecycle.
Why Do Lasers Require Chillers?
A typical laser cooling system integrates a temperature controller, a coolant pump, and a heat exchanger. These components work together to manage the heat generated during operation. However, a more advanced system, incorporating a compressor, condenser, capillary throttle, and evaporator, offers even greater precision and efficiency.
How Does Temperature Impact Laser Performance?
Heat directly affects laser performance by reducing optical conversion efficiency and beam precision. Overheating can distort components, degrade laser output, and diminish overall quality.
The Importance of Chiller Accuracy
Precision Cooling:
High-performance chillers ensure precise temperature control, essential for maintaining the accuracy of laser beams and preventing component warping.
Pulsation-Free Pumps:
Systems with pulsation-free pumps minimize vibrations, preserving beam focus and delivering superior performance.
Do Different Lasers Have Unique Cooling Requirements?
Yes. Industrial lasers demand robust cooling systems capable of maintaining strict temperature ranges. Refrigerated recirculating chillers, equipped with thermostatic or solenoid expansion valves, are designed to meet these needs by offering high precision and stability.
Applications of Laser Technology Today
Lasers are indispensable across industries for tasks such as:
- Spectroscopy: Advanced material analysis.
- Heat Treatment: Strengthening materials.
- Barcode Readers: Seamless retail operations.
- Material Processing: Welding, cutting, and marking.
Advantages of Lasers
- High Data Transfer Capability: Widely used in telecommunications.
- Compact Data Storage: Lasers enable the storage of vast amounts of data in small spaces, making them essential for CDs, DVDs, and other media.
- Precision in Treatments: Medical and cosmetic lasers allow for targeted and efficient procedures.
Final Thoughts
Cooling systems are indispensable for lasers, ensuring they operate efficiently and maintain high precision. The right chiller system not only extends the laser’s lifespan but also enhances its performance, making it a must-have for any laser application. Whether for industrial, medical, or everyday use, selecting the appropriate chiller is key to unlocking the full potential of laser technology.