When it comes to refrigeration technologies, semiconductor (thermoelectric) and compressor-based systems are two popular options. Both have distinct cooling mechanisms and advantages, making them suitable for various applications. This article explores the key differences, how each technology works, and which option might be best for your needs.
The Fundamental Difference
- Compressor Refrigeration:
Utilizes refrigerant gases like Freon. The gas is compressed and released into coils, where it dissipates heat. This cycle creates cooling through a vapor-compression process. - Semiconductor Refrigeration:
Uses solid-state Peltier devices. When electricity flows through these devices, one side becomes hot, and the other becomes cold, providing cooling without any moving parts or refrigerants.
Compressor-Based Technology: How It Works
Compressor systems rely on a closed-loop cycle with four main components: compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Here’s the process:
- The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas.
- The gas moves to the condenser, where it cools and condenses into a liquid.
- The liquid passes through an expansion valve, where it undergoes rapid cooling.
- The refrigerant absorbs heat from the surroundings in the evaporator, completing the cycle.
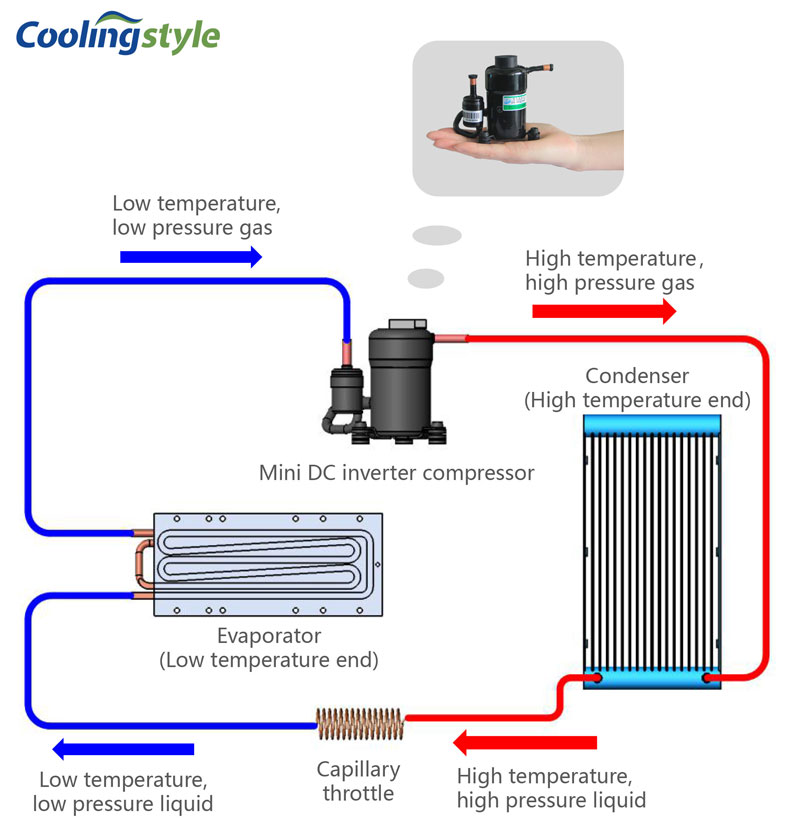
Advantages of Compressor-Based Systems:
- High cooling efficiency, especially for large spaces.
- Affordable and easy to maintain.
- Reliable for industrial and commercial settings.
- Long lifespan.
Applications:
- Supermarkets, restaurants, and industrial refrigeration.
- Automotive air conditioning.
- Marine refrigeration.
Thermoelectric Semiconductor Technology: How It Works
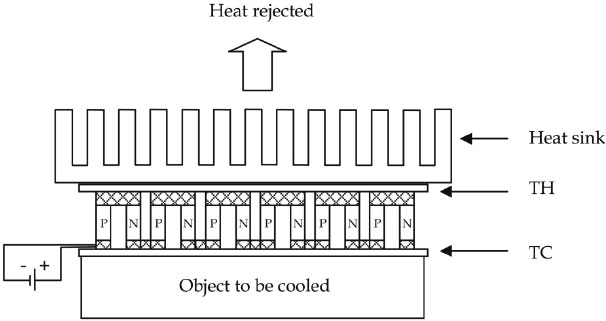
Thermoelectric technology relies on the Peltier effect, where electricity creates a temperature differential across two ceramic materials. This results in one side becoming hot and the other cold. The heat is dissipated via heatsinks, while the cold side cools the target area.
Advantages of Thermoelectric Systems:
- Solid-state design with no moving parts ensures durability and minimal wear.
- Environmentally friendly—no refrigerants or chemicals.
- Compact and easy to integrate into small systems.
Limitations:
- Less efficient than compressor systems at high cooling loads.
- Performance decreases with rising ambient temperatures.
- Often heavier and bulkier than compressor-based units.
Applications:
- Medical refrigeration and laboratory equipment.
- Low-temperature cooling in food storage and solar applications.
- Data centers and telecommunications.
Comparing the Two Technologies
| Feature | Compressor-Based | Thermoelectric (Semiconductor) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Affordable | Generally higher |
| Maintenance | Easy, with periodic servicing | Minimal due to lack of moving parts |
| Cooling Capacity | Suitable for large loads | Best for low to medium loads |
| Environmental Impact | Uses refrigerants | Eco-friendly, no refrigerants |
| Size and Weight | Compact options available | Can be bulkier |
| Temperature Range | Effective at all ranges | Best below room temperature |
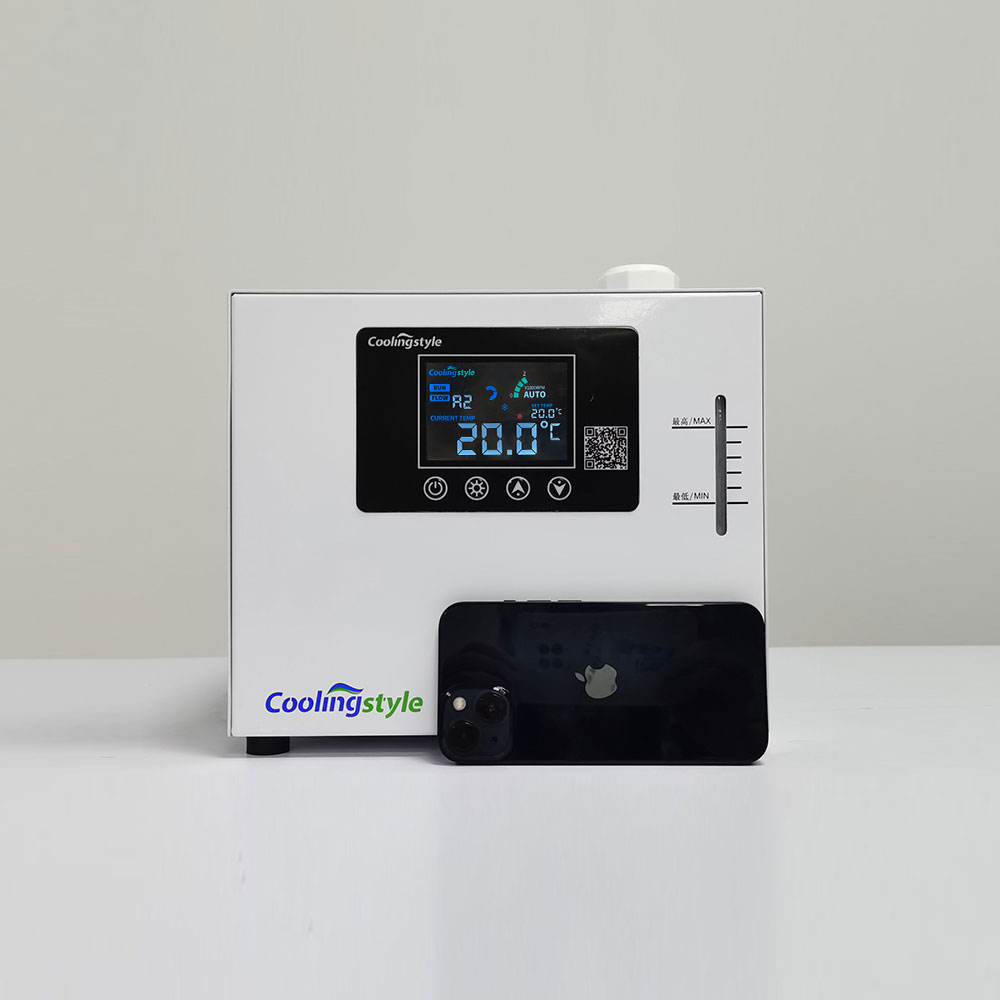
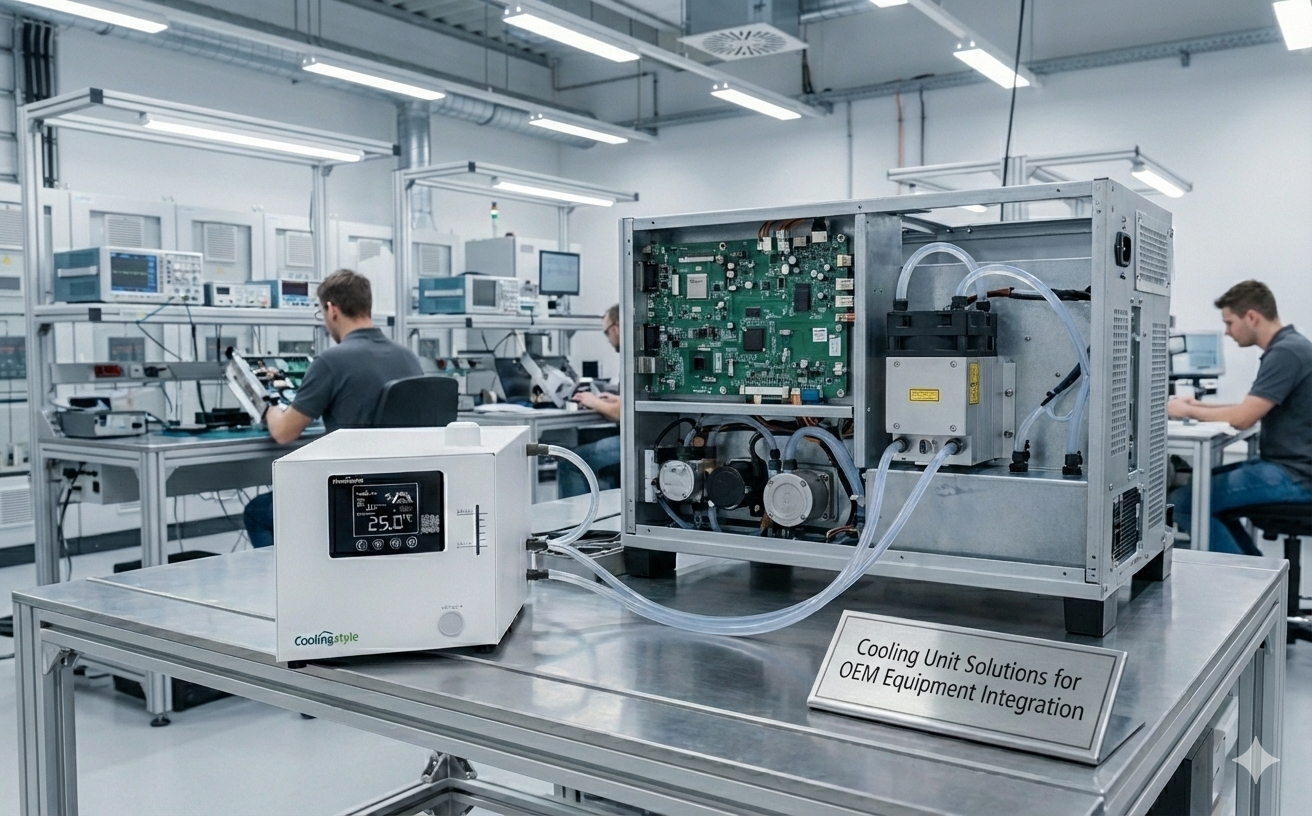
The Coolingstyle Advantage
Coolingstyle bridges the gap between compressor and thermoelectric technologies with DC variable frequency inverter compressor chillers. These innovative systems offer the following benefits:
- Dual Power Options: Compatible with DC and AC power sources.
- Variable Control: Intelligent conversion control for precise operation.
- Compact Design: Lightweight and space-saving.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower energy consumption with high cooling performance.
- Enhanced Reliability: Minimal maintenance needs and long lifespan.
- Customizable Power: Options for DC24V, AC110V, or AC220V power input.
Specifications of Coolingstyle Chillers:
| Cooling capacity | 420W/580W |
| Compressor type | DC variable frequency inverter compressor |
| Chiller size | 13.6*9.8*8.5in |
| Net weight | 10kg |
| Rated power | 250W |
| Temperature control accuracy | ±0.1℃ |
| Refrigerant | R134a |
| Power | DC24V or AC110 or 220V is available |
Conclusion
Both compressor-based and thermoelectric semiconductor chillers have their unique advantages. Compressor systems are ideal for high-capacity, large-scale cooling needs, while thermoelectric systems are perfect for compact, low-temperature applications.
Why choose Coolingstyle?
Coolingstyle’s DC inverter chillers combine the best of both worlds—offering high efficiency, precise temperature control, and a compact design, making them a versatile solution for diverse applications.
Need help deciding? Contact Coolingstyle to find the perfect chiller for your needs!







1 thought on “Semiconductor vs. Compressor Refrigeration: What’s Best for Your Application?”
I am to purchase a wine cooler where both systems are available.
I live in FNQ with high humidity part of the year.
Can you give me your take on which system to go for and why.
Thank you
Jim