Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is rapidly expanding across various industries. From creating prototypes to manufacturing durable and reliable products, 3D printing is becoming indispensable. However, the heat generated during the printing process—especially when producing intricate designs—can harm the printer and affect the quality of the prints. Without an efficient cooling system, you may face issues like overheating, reduced print quality, and even equipment damage.
This article will guide you through the importance of 3D printer cooling systems, the types available, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
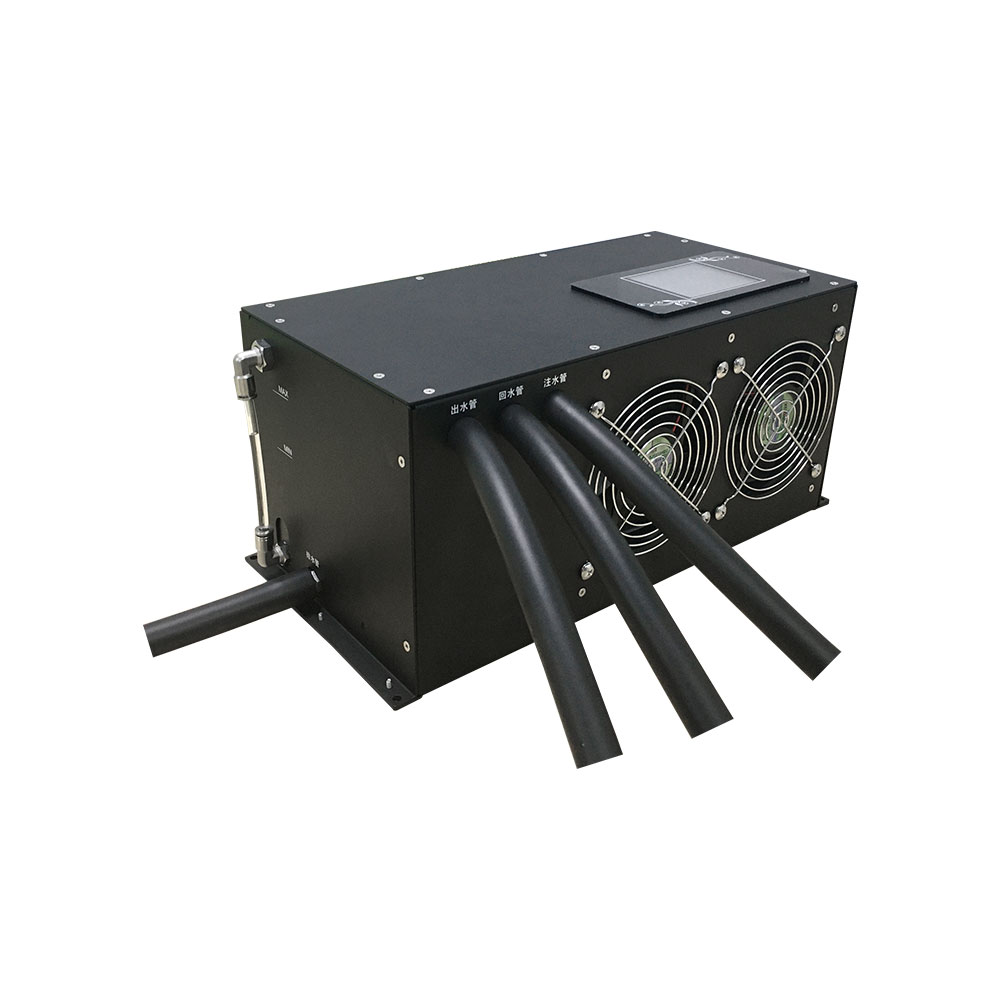

Why Do You Need a Cooling System?
3D printers work by layering materials like PLA thermoplastics until a solid structure forms. As this process involves high temperatures, particularly for more complex designs, adequate cooling is essential. A cooling system helps regulate heat and improves overall efficiency in the following ways:
- Improved Print Quality: Cooling enhances bridging and overhang performance, preventing defects like sagging or stringing.
- Prevents Equipment Damage: Heat imbalances can damage the printer’s internal components, shortening its lifespan.
- Stabilizes Print Process: Proper cooling ensures consistent performance regardless of environmental temperatures.
For example, without effective cooling, the material may deform as it cools unevenly. This is especially crucial when working with overhangs or steep angles.
Parts of a 3D Printer Requiring Cooling
Cooling systems can be applied to several components of a 3D printer:
- Control Board: Essential circuitry like the CPU and motor drivers need cooling to prevent overheating.
- Hot End: A cooling fan is often positioned near the cold side of the hot end to prevent overheating except for the heater and nozzle.
- Printed Parts: Part cooling fans direct cool air under the nozzle, ensuring newly extruded plastic hardens quickly.
- Power Supply: Internal fans cool high-power transistors, resistors, and transformers under heavy loads.
- Motors: Although less common, stepper motors may include a fan or condenser for temperature regulation.
Do you need cooling for all these parts?
In most cases, yes. However, the motor rarely requires additional cooling, and power supplies typically include built-in cooling fans, so no modifications are necessary.
How to Choose the Right Cooling System
Selecting the ideal cooling system for your 3D printer involves considering several factors:
1. Cooling Capacity
Measure the heat your printer generates and choose a system with sufficient cooling capacity, typically stated in kilowatts (kW) or BTU/hr. Consider additional factors like the discharge temperature of the coolant.
2. Air-Cooled vs. Water-Cooled
- Air-Cooled Systems: Use fans to dissipate heat. They are cost-effective and simple to install but may struggle with high temperatures.
- Water-Cooled Systems: Use liquid coolant to absorb and transfer heat. They offer superior performance in high-temperature applications.
3. Electrical Compatibility
Ensure the system is compatible with your printer’s power supply, voltage, and frequency (50 Hz, 60 Hz, or both). Proper electrical setup ensures consistent performance.
4. Communication Link
Advanced cooling systems can connect to 3D printers, allowing real-time monitoring of water temperature, setpoints, and operational status.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose a cooling system that ensures reliable performance and protects your investment.
Types of 3D Printer Cooling Systems
1. Air Cooling Systems (Fans)
Air cooling is the simplest and most common cooling method. Fans move airflow to dissipate heat, either by pushing cool air into overheated areas or drawing hot air away.
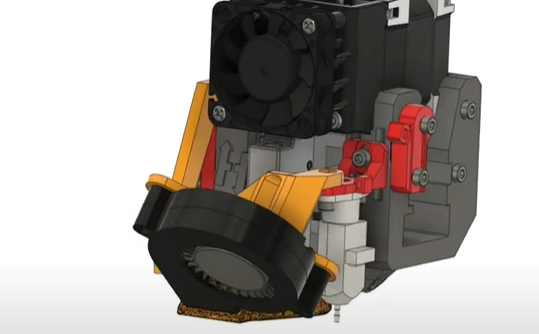
- Layer Fan: A small fan installed on the printer head, directing air at freshly extruded plastic to cool it quickly. Proper layer fan speed improves print quality by preventing deformation.

Best Materials for Layer Fan Use:
- PLA, PETG, PP, and PVA benefit greatly from layer fans.
- ABS and ASA, however, are sensitive to sudden temperature changes, making fans unsuitable unless the printer is fully enclosed.
Limitations:
Air cooling may not suffice for high-temperature printing or heavy-duty applications, as fans cannot cool components efficiently in extreme conditions.
2. Water Cooling Systems
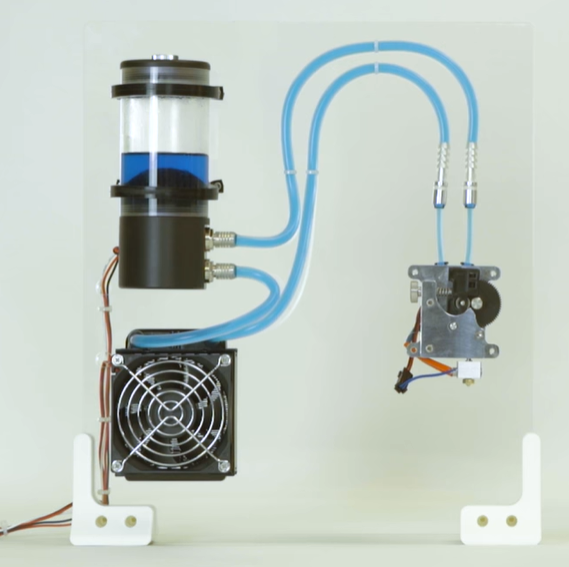
Water cooling uses liquid coolant to absorb and dissipate heat. The coolant circulates through the machine, transferring heat from the engine to a radiator where it cools before recirculating.
Advantages of Water Cooling:
- Handles high power requirements and extreme heat effectively.
- Provides consistent cooling, even under heavy loads.
- Improves print speed and quality by maintaining stable temperatures.
Best Applications:
Water cooling is ideal for printers operating at temperatures above 210°C or in high-temperature environments. It is especially effective for large, industrial-grade 3D printers.
Comparing Air and Water Cooling
| Feature | Air Cooling System | Water Cooling System |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Efficiency | Limited for high temperatures | Superior heat dissipation |
| Maintenance | Simple (cleaning fans) | Requires monitoring of coolant levels |
| Noise | Can be noisy | Quieter operation |
| Compatibility | Suitable for small-scale printers | Best for industrial or high-temp printers |
Conclusion
Choosing the right cooling system for your 3D printer can significantly impact its performance and the quality of your prints. While air cooling systems (like fans) are economical and effective for most hobbyist printers, water cooling systems excel in high-power or high-temperature environments, delivering faster printing speeds and better results.
By understanding your printer’s requirements and evaluating the available options, you can ensure long-term reliability and optimal performance for your 3D printing projects.






1 thought on “Master 3D Printing Efficiency: Choose the Perfect Cooling System for Your Printer”
How does heat impact the 3D printing process, and what cooling solutions can prevent overheating and ensure high-quality prints?
Regard IT Telkom