As machinery, engines, and electronics work harder than ever, overheating has become a significant issue, impacting efficiency and longevity. Enter the micro refrigeration system, a small yet powerful cooling solution designed to manage heat effectively in compact spaces. In this article, we’ll break down the key aspects of micro refrigeration systems, how they work, their applications, and why they are essential for modern equipment.
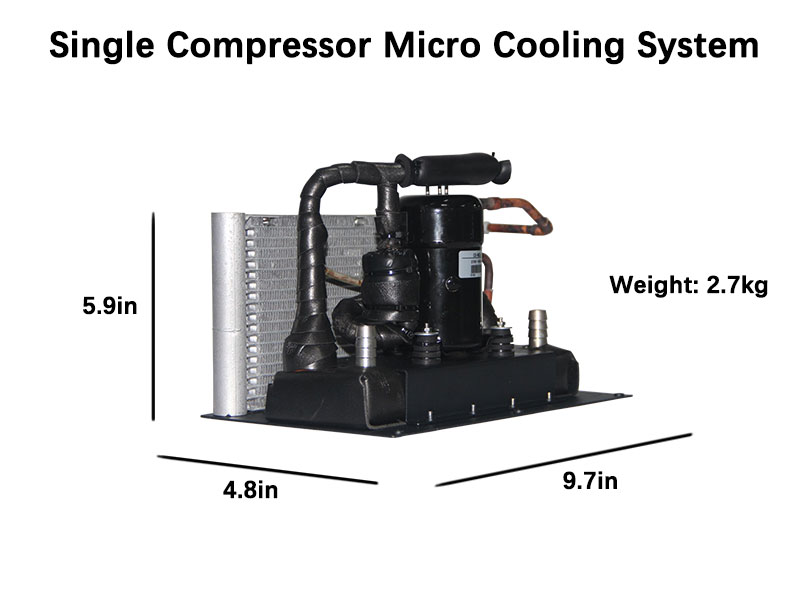
What is a Micro Refrigeration System?
A micro refrigeration system is a compact cooling unit that helps maintain optimal temperatures for machinery and electronics, preventing overheating and performance degradation.
Key Features:
- Compact size and lightweight structure
- Utilizes tiny DC inverter compressors with variable speeds
- Provides stable and efficient thermal management
- Supports cooling for equipment like motors, laser devices, medical systems, and more
Applications:
- Healthcare: Medical device cooling
- Electronics: Personal and industrial cooling systems
- Industrial Equipment: Printing machines, engines, and 3D printers
- Specialized Uses: Laser beam cooling, water chillers, and beauty appliances
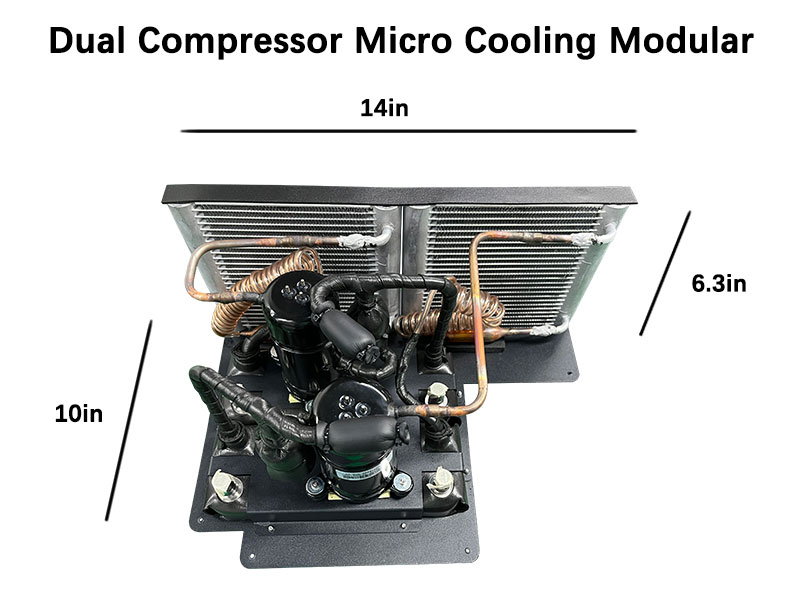
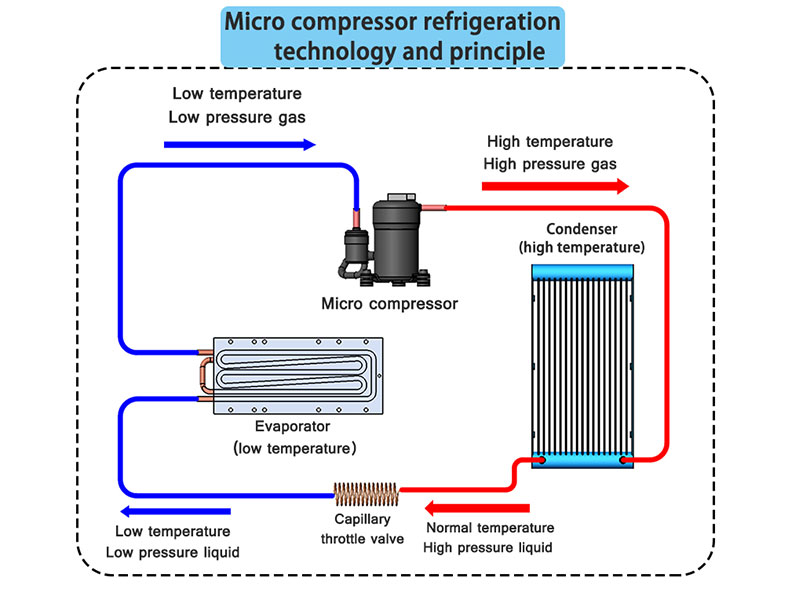
How Does a Micro Refrigeration System Work?
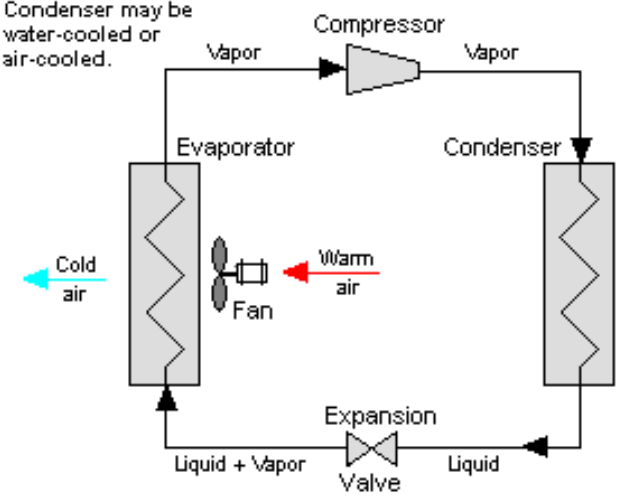
A micro refrigeration system operates using a vapor compression refrigeration cycle, just like traditional systems but scaled down for smaller applications.
Key Components:
- Compressor: Increases refrigerant pressure and temperature.
- Condenser: Dissipates heat into the surrounding environment.
- Expansion Valve: Reduces refrigerant pressure and temperature.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the equipment being cooled.
Working Process:
- The compressor compresses low-pressure refrigerant into a high-pressure, high-temperature state.
- This refrigerant flows to the condenser, where it releases heat into the environment and transitions into a liquid state.
- The liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature.
- The low-temperature refrigerant absorbs heat from the equipment via the evaporator, cooling the system.
- The cycle repeats, ensuring consistent cooling.
This efficient heat transfer process is what makes micro refrigeration systems ideal for compact, high-performance equipment.
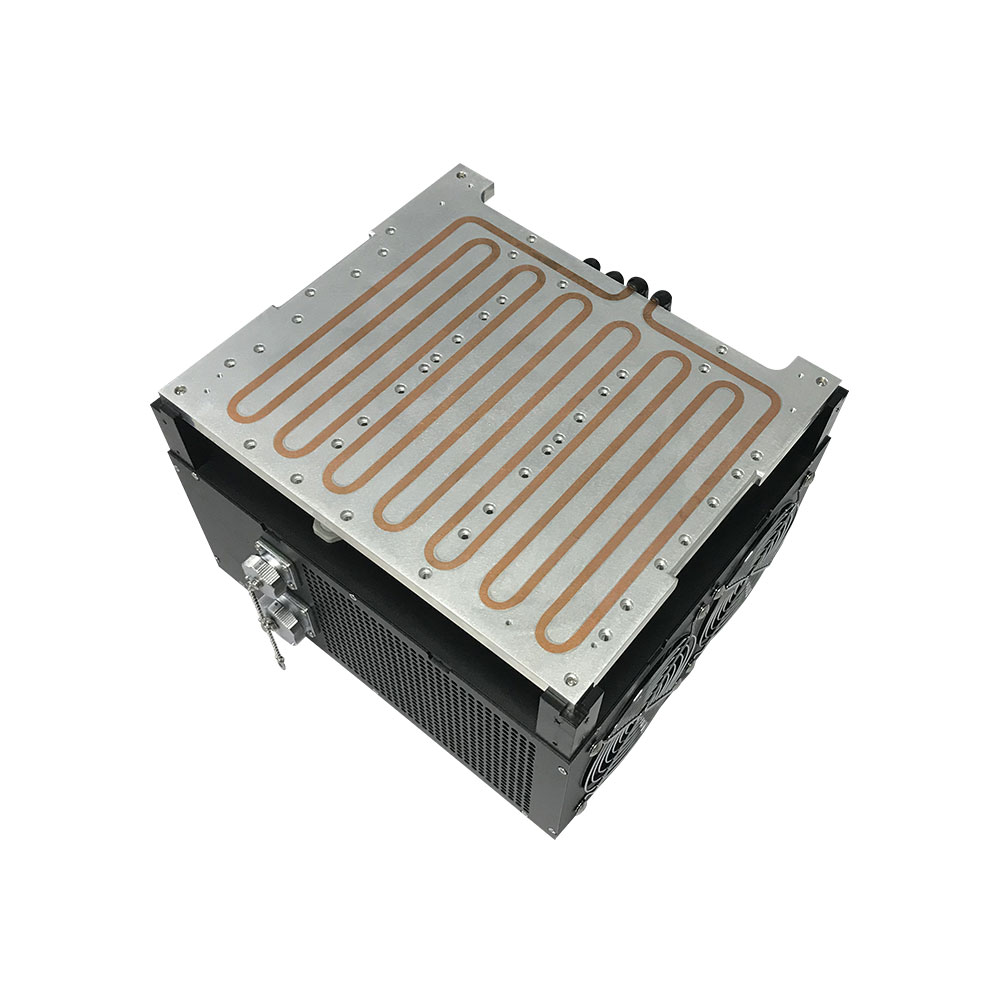
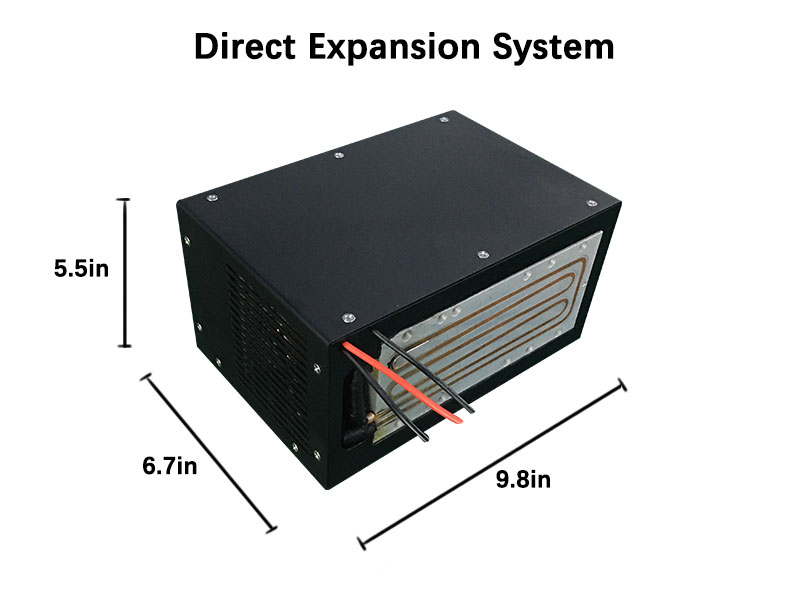
Applications of Micro Refrigeration Systems
1. Laser Cooling
Maintains stable temperatures for laser equipment to ensure precise operations and prolonged lifespan.
2. Medical Devices
Essential for cooling medical equipment like imaging systems and therapy devices.
3. Electronics and Industrial Use
Prevents overheating in high-power electronics and machinery like 3D printers, printing machines, and engines.
4. Personal Cooling Systems
Portable solutions for individual cooling needs, such as wearable devices.
5. Compact Cooling Units
Used in systems like water chillers, glycol refrigeration units, and portable air conditioners.


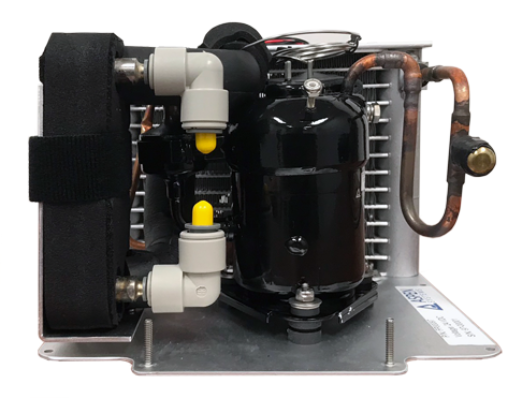
Advantages of Micro Refrigeration Systems
1. Compact and Lightweight
Designed to save space, making them perfect for small and portable applications.
2. Energy Efficiency
Consumes less power while delivering excellent cooling capacity, lowering operational costs.
3. High Thermal Performance
Provides efficient heat transfer and stable thermal management for high-heat applications.
4. Versatility
Adaptable for various applications, including industrial, medical, and personal uses.
5. Cost-Effective
More affordable than larger-scale cooling systems, without compromising performance.
Advanced Micro Refrigeration Systems
1. Vapor Compression Refrigeration Systems
These systems utilize refrigerants to provide high cooling efficiency and are known for their:
- Compact size
- High cooling output
- Reliable performance in extreme conditions
Applications of Vapor Compression Refrigeration Systems:
- Healthcare and Medical Devices:
- Cooling systems for diagnostic machines, surgical tools, and patient therapy devices.
- Aerospace and Defense:
- Keeps avionics, radar systems, and sensitive military electronics at optimal operating temperatures.
- Electronics and Semiconductor Industry:
- Manages heat dissipation in CPUs, GPUs, and high-performance computing systems.
- Industrial Applications:
- Supports high-precision machinery such as CNC milling machines, printing machines, and robotics.
- Scientific Equipment:
- Essential for maintaining stable conditions in laboratory instruments like spectrometers and electron microscopes.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Used in compact and portable cooling solutions for laptops, gaming systems, and personal devices.
- Automotive Industry:
- Provides cooling for electric vehicle batteries and in-car electronics.
2. Liquid Chiller Systems
A form of micro refrigeration, liquid chillers are widely used for precise temperature control.
Features:
- Uses miniature compressors for efficient cooling
- Provides excellent heat exchange through compact designs
- Delivers stable performance for applications requiring precise thermal management
Applications:
- Cooling high heat flux components
- Laser cooling systems
- Scientific and industrial refrigeration

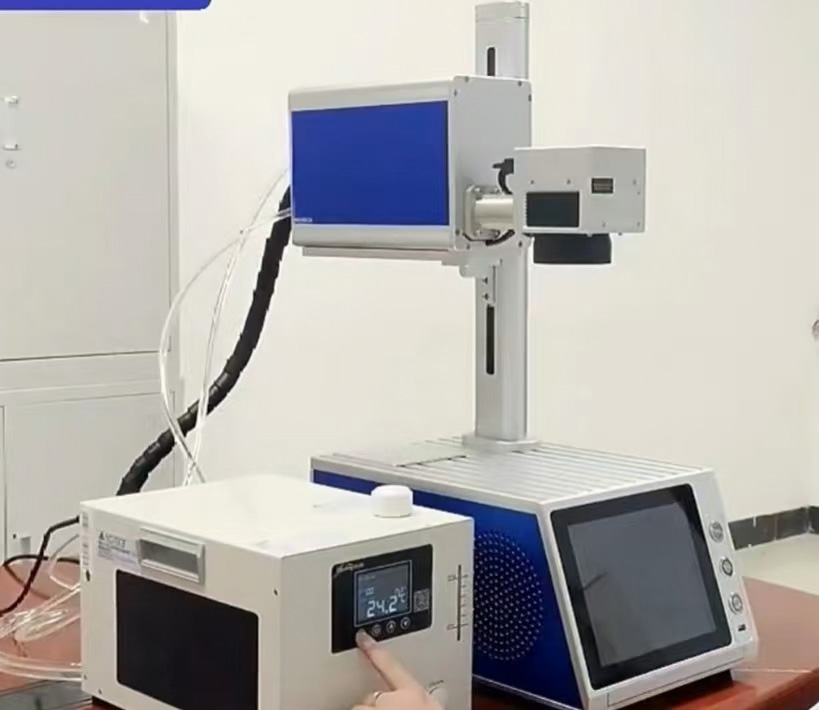
Why Choose Coolingstyle’s Micro Refrigeration Systems?
Coolingstyle is at the forefront of micro refrigeration innovation, offering reliable, efficient, and compact solutions tailored for various applications.
Key Features:
- Compact Design: Saves space and is easy to integrate into existing systems.
- Precision Temperature Control: Maintains stability within ±0.1°C.
- Energy Efficient: Consumes less power, reducing operational costs.
- Versatile Power Options: Supports AC, DC, and battery-powered configurations.
- Durability and Reliability: Built for long-term use in demanding environments.
Recommended Products:
Rack-Mounted Chiller: Perfect for space-constrained setups requiring robust performance.
Micro Water Chiller: Ideal for laser cooling and compact industrial applications.
Conclusion
A micro refrigeration system is a game-changing solution for efficient and compact cooling. Whether you need to cool medical devices, high-power electronics, or industrial machinery, these systems deliver exceptional performance with minimal space and energy requirements.
For cutting-edge cooling technology, Coolingstyle’s micro refrigeration systems stand out as a reliable choice, combining innovation, efficiency, and affordability. Explore your options today and keep your equipment running at peak performance!







1 thought on “All You Need to Know About Micro Refrigeration Systems: Compact Cooling Redefined”
How do I purchase this item?
I’m pregnant and love to have this item with summer coming up!