Are you struggling to understand how air-cooled chillers operate to optimize your cooling system? Discover the secrets to enhance your efficiency.
Air-cooled chillers achieve efficient temperature control through refrigerant cycles and air heat dissipation. They use key components like compressors, evaporators, condensers, expansion valves, and control systems to cool industrial and commercial environments effectively.
Delving into their working mechanism will help you better apply and maintain the equipment.
What Are the Main Components of an Air-Cooled Chiller?
Curious about the inner workings of air-cooled chillers but feeling overwhelmed? Let’s break down the essential parts for clarity.
The main components include the compressor, evaporator, condenser, expansion valve, and control system. Each plays a critical role in the refrigeration cycle, ensuring efficient cooling performance.
Air-cooled chillers consist of several key components that work together to remove heat from a process or space:
- Compressor: Acts as the heart of the system, compressing refrigerant gas and raising its pressure.
- Evaporator: Allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the water or process fluid, turning it into vapor.
- Condenser: Equipped with fans and finned coils to dissipate absorbed heat into the surrounding air, condensing the refrigerant back into a liquid.
- Expansion Valve: Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, reducing its pressure and temperature.
- Control System: Manages the operation of the chiller, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Understanding these components helps in troubleshooting and maintaining the chiller effectively.
What Is the Workflow of an Air-Cooled Chiller?
Confused about how all the parts come together in an air-cooled chiller? Let’s simplify the workflow for better understanding.
The refrigerant circulates through the system, absorbing heat from the evaporator and releasing it through the condenser to the air, completing the cooling process efficiently.
The workflow involves a continuous refrigeration cycle:
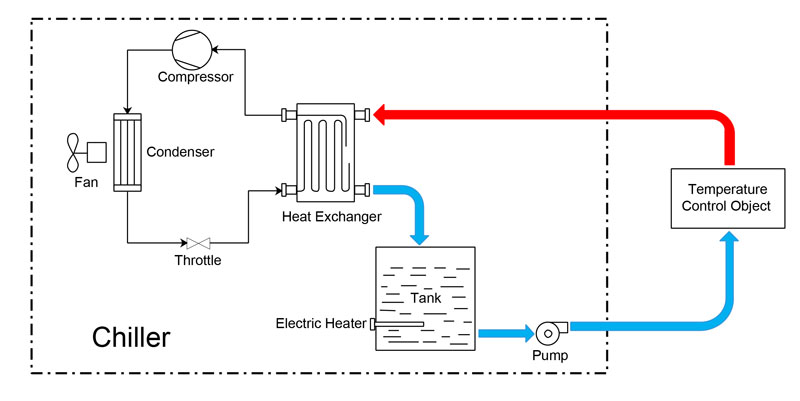
- Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the chiller. It compresses low-temperature, low-pressure refrigerant gas into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas, which is then sent to the condenser. The compressor powers the entire cooling cycle.
- Fan and Condenser: The high-temperature gas enters the condenser, where the fan blows air to remove heat. As the refrigerant cools down, it condenses into a liquid.
- Expansion Valve: The high-pressure refrigerant liquid passes through the expansion valve, where its pressure drops sharply. This turns the refrigerant into a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid, preparing it for the evaporator.
- Evaporator: In the evaporator, the low-pressure liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from the water in the water tank, causing the refrigerant to evaporate into a gas. During this process, the water temperature drops, and the refrigerant takes away the heat from the water.
- Water Tank and Water Pump: The cooled water is stored in the water tank. The water pump circulates the cold water to the target object (such as a laser machine or medical device). The pump ensures that the water flows continuously between the chiller and the target, keeping the temperature stable.
- Heating Rod (if the chiller has heating capability): When the surrounding temperature is lower than the set value, the heating rod can provide heat to prevent the water from getting too cold. This ensures that the water temperature remains stable even in cooler environments.
- Target Object: The chilled water flows through the target object (like a laser cutter or electronic device), absorbing its heat. The water then returns to the chiller to be cooled again, keeping the target at the desired temperature and preventing overheating.
The entire process is controlled by a temperature controller. When the temperature of the target object goes above the set range, the chiller starts the cooling cycle. If the temperature drops too low, the heating rod kicks in to maintain the ideal temperature. This system ensures stable, reliable temperature control, making air-cooled chillers perfect for applications requiring continuous cooling.
How Does the Refrigerant Function in an Air-Cooled Chiller?
Unsure about the role of refrigerant in your chiller system? Understanding this can enhance your system’s efficiency.
The refrigerant is crucial, absorbing and releasing heat through phase changes, driving the cooling cycle in air-cooled chillers effectively.
In an air-cooled chiller, the refrigerant acts as the medium for heat transfer:
- Heat Absorption: In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the process fluid, evaporating into a gas.
- Compression: The gaseous refrigerant is compressed, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Heat Release: In the condenser, the refrigerant releases the absorbed heat to the ambient air as it condenses back into a liquid.
- Cycle Continuation: This cycle of evaporation and condensation allows continuous removal of heat from the process fluid.
This process maintains effective cooling by transferring heat from the inside to the outside environment.
What Are the Advantages of Air-Cooled Chillers?
Debating whether an air-cooled chiller is right for you? Let’s explore the benefits to help you decide.
Air-cooled chillers offer easy installation, low maintenance costs, and no need for a water source, making them suitable for various environments.
Advantages include:
- No Cooling Tower Needed: Eliminates the need for additional infrastructure, reducing costs.
- Water Conservation: Ideal for areas with limited water supply or high water costs.
- Ease of Installation: Simpler setup compared to water-cooled systems.
- Low Maintenance: Fewer components mean less upkeep and lower operating expenses.
- Flexibility: Suitable for various sizes and types of facilities, from small commercial spaces to medium industrial applications.
These benefits make air-cooled chillers a practical choice for many cooling needs.
What Is the Best Installation Location for an Air-Cooled Chiller?
Concerned about where to place your air-cooled chiller for optimal performance? Let’s find the ideal spot.
A well-ventilated outdoor or rooftop location enhances heat dissipation and efficiency for air-cooled chillers.
Ideal locations include:
- Open Areas: Spaces with ample airflow to allow effective heat dissipation.
- Rooftops: Elevated positions prevent obstructions and facilitate better air circulation.
- Ground-Level Pads: Outdoor sites away from walls or other structures that might block airflow.
Ensure:
- Adequate Clearance: Follow manufacturer guidelines for space around the unit.
- Avoid Heat Sources: Place away from exhaust vents or other heat-generating equipment.
- Protection from Elements: Consider environmental factors like debris, dust, and weather conditions.
Proper placement maximizes efficiency and prolongs the unit’s lifespan.
How to Properly Maintain an Air-Cooled Chiller?
Worried about keeping your chiller running smoothly? Effective maintenance is key to longevity.
Regular cleaning, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical components ensure long-term efficient operation of air-cooled chillers.
Maintenance tips include:
- Condenser Cleaning: Remove dust and debris from coils to maintain heat transfer efficiency.
- Refrigerant Checks: Regularly monitor levels to detect leaks or deficiencies.
- Electrical Inspection: Tighten connections and check for signs of wear or damage.
- System Monitoring: Keep an eye on pressures and temperatures to identify potential issues early.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule routine check-ups with qualified technicians for comprehensive assessments.
Consistent maintenance prevents breakdowns and keeps the system operating at peak efficiency.
What Applications Are Air-Cooled Chillers Suitable For?
Uncertain if an air-cooled chiller fits your industry? Let’s explore where they excel.
Air-cooled chillers are widely used in commercial buildings, data centers, manufacturing industries, and other fields requiring reliable cooling.
Common applications include:
- Commercial HVAC Systems: Providing comfort cooling for offices, hotels, and retail spaces.
- Data Centers: Cooling critical equipment to prevent overheating and ensure uptime.
- Industrial Processes: Supporting manufacturing operations like plastic molding, metal plating, and chemical processing.
- Medical Facilities: Cooling imaging equipment and maintaining controlled environments.
- Food and Beverage Industries: Preserving products through precise temperature control.
Their versatility and ease of installation make them suitable for a broad range of settings.
At Coolingstyle, we offer a range of air-cooled chillers tailored for laser applications:
- Laser Types:
- Nanosecond UV Lasers
- Nanosecond Green Lasers
- Nanosecond Infrared Lasers
- Picosecond UV Lasers
- Picosecond Green Lasers
- Picosecond Red Lasers
- CS-ARC-Q420A110/A111 (Cooling Capacity: 420W-580W):
- CS-ARC-Q580A110/A111 (Cooling Capacity: 580W):
- CS-ARC-Q4U02A110/A111 (Cooling Capacity: 500W-600W):
- CS-AMC-Q5U3A110 (Cooling Capacity: 1200W):
- CS-ARC-M160A410 (Cooling Capacity: 1600W):
- CS-ARC-M270A410 (Cooling Capacity: 2700W):
Our chillers are designed to meet specific cooling requirements of various laser systems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Learn more about Coolingstyle’s products or contact us for personalized solutions.
What Are Common Faults and Solutions for Air-Cooled Chillers?
Experiencing issues with your chiller? Knowing common faults can help you troubleshoot effectively.
Common faults include refrigerant leakage and component aging; regular maintenance can effectively prevent them, ensuring stable operation.
Common issues:
- Refrigerant Leaks: Lead to decreased efficiency; detected through pressure tests and resolved by repairing leaks and recharging refrigerant.
- Component Wear: Aging compressors or fans may fail; preventive replacement avoids unexpected downtime.
- Condenser Fouling: Dirt buildup reduces heat transfer; regular cleaning restores performance.
- Electrical Problems: Faulty wiring can cause malfunctions; routine inspections prevent failures.
Implementing a maintenance program addresses these faults, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding how air-cooled chillers work and how to maintain them helps optimize cooling efficiency and extend equipment life. Whether for industrial or commercial use, these insights enable you to meet your cooling needs effectively.




