Philip Preston, president of PolyScience talks about chiller temperature control as a key factor affecting laser stability.
According to the research, the CO2 RF laser photoelectric conversion efficiency is about 10% to 20%, the rest of the energy will be converted to waste heat.
If the discharge area of the CO2 RF laser cannot be effectively dissipated, the gas temperature in the discharge area will continue to rise.
This will cause the thermal motion of molecules in the discharge area to intensify with the increase of temperature, causing the depletion of molecules in the upper energy level, which will trigger the broadening of the CO2 molecular spectrum, and eventually affect the stability of the laser output power or make its output power decrease.
Therefore, it is particularly important to dissipate excess heat from the laser by external assistance.

Recent studies show that the photoelectric conversion efficiency is higher when laser gas temperature of CO2 RD laser between 400 ~ 500K.
Common ways to dissipate heat from lasers
When using RF lasers, there are two types of heat dissipation methods that are usually used, air-cooled heat dissipation and water-cooled heat dissipation.
Air-cooled cooling is commonly used for low-power lasers, which generally do not exceed 100 W. Water-cooled cooling covers the entire power range that CO2 lasers can achieve.


The above two heat dissipation methods have one thing in common, that is, both do not directly cool the discharge area that generates heat, but conduct the waste heat generated in the discharge area to the coolant or heat sink plate by conduction.
Prolong CO2 Laser Tube Lifetime with a Laser Water Chiller

Lasers help to engrave many types of objects. Therefore, laser-gravures have become indispensable components to modern manufacturing facilities. The performance and life span of laser engraving equipment vary depending on different factors including frequency and cleaning. However, many people neglect the crucial factor that ensures long-term performance of the machines: efficient heating and cooling. The use of lasers for water cooling can prolong the life of the tubes and increase efficiency.
Effect of coolant temperature on the laser
For water cooling, we usually use pure water, distilled water or deionized water as the coolant (antifreeze coolant is also available in winter) to dissipate heat from the laser.
According to Newton’s law of cooling: Φ=A*η*Δt.
Where Φ is the heat dissipated; A is the area of the heat sink, η is the heat transfer coefficient, and Δt is the temperature difference.
It can be concluded that after the structure and material of the CO2 laser is determined, the main factor affecting the heat dissipation is the temperature difference (the temperature difference here refers to the temperature difference between the coolant temperature and the temperature of the laser discharge area).
Taking pure water as an example, assuming that the temperature of the coolant rises, then it and the temperature difference between the discharge area will be reduced, the cooling effect decreases, and ultimately affect the laser power. According to some of the experimental data show that the coolant (pure water) temperature increases by about 1 ℃, the laser power will be reduced by about 0.5% to 1%.
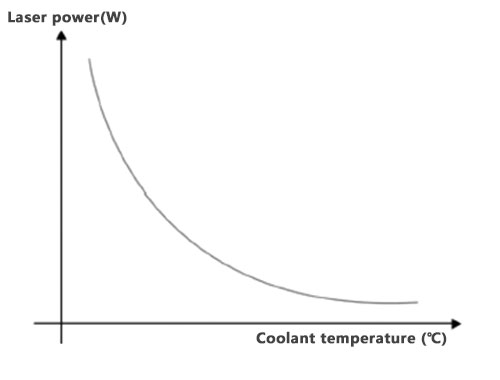
Therefore, lowering the temperature of the coolant improves heat dissipation, which in turn increases laser power.
So, can the coolant temperature be lowered infinitely? The answer is obviously no. For some CO2 lasers, if the cooling temperature is too low, a longer warm-up time is required, which reduces the working efficiency.
The most common effect is that the coolant temperature is too low, which can lead to condensation on the laser surface, affecting the laser’s use and even shortening its service life.
Coolant and stable laser power
Obviously, we need a relatively stable CO2 laser gas temperature in order to get a stable laser power from a CO2 laser. Ultimately, that means stable heat dissipation.
From Newton’s law of cooling (Ф = Α*η*Δt), we can see that the key factor to obtain stable heat dissipation is a constant stable temperature difference (Δt). Therefore, temperature stability is essential in the process of actual production operations. The precise temperature control will help the laser to obtain a stable output power.
What kind of water chiller to choose?
Considering the two factors of laser power and stability, Coolingstyle recommends the water chillers below to enhance the laser systems power stability. The water chillers are especially designed for the laser industry.
The features of Coolingstyle water cooling chillers are as below:
- The cooling capacity varies from 200W to 1200W.
- Temperature control stability is ±0.1℃.
- Smaller size and lighter weight.
- Easy to maintain
- Low wattage consumption.
Different cooling capacity chillers to choose
- 420W and 580W Cooling capacity
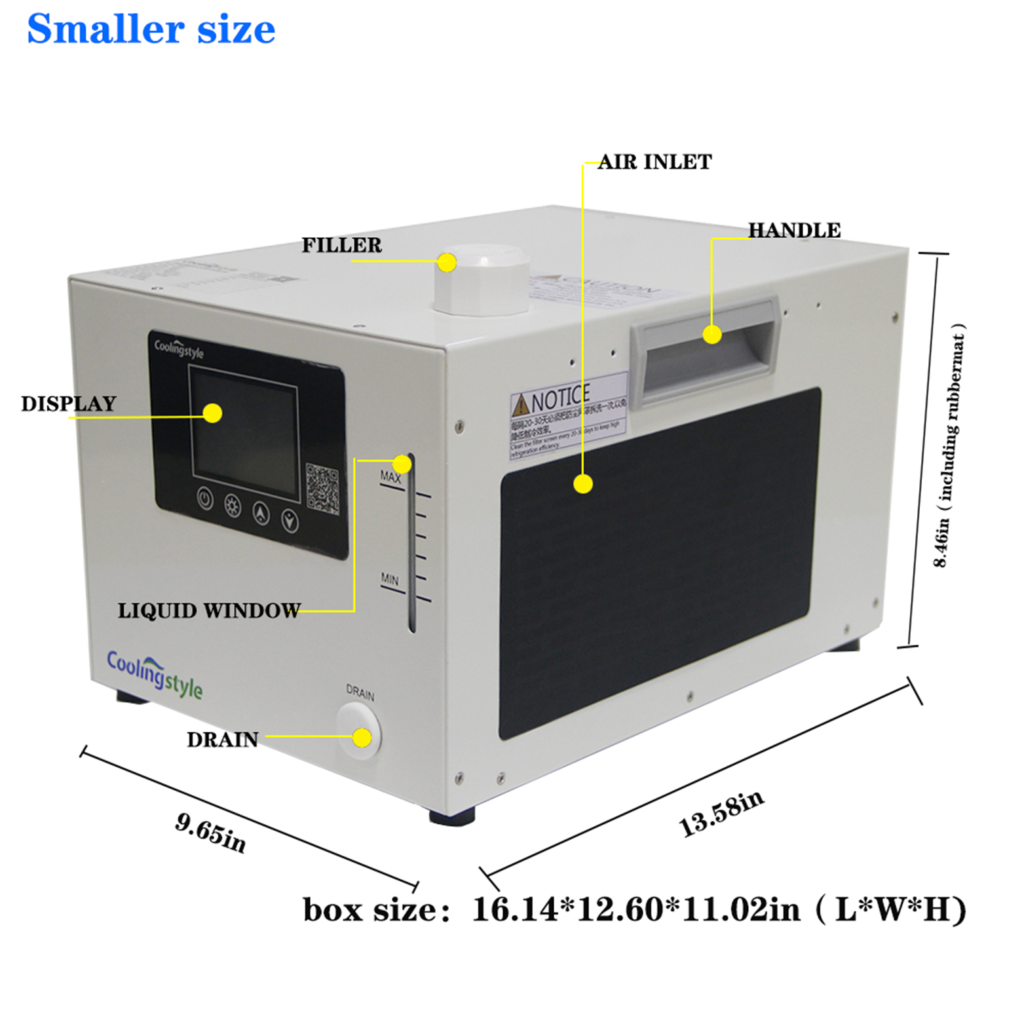

2. 400W and 500W cooling capacity chiller
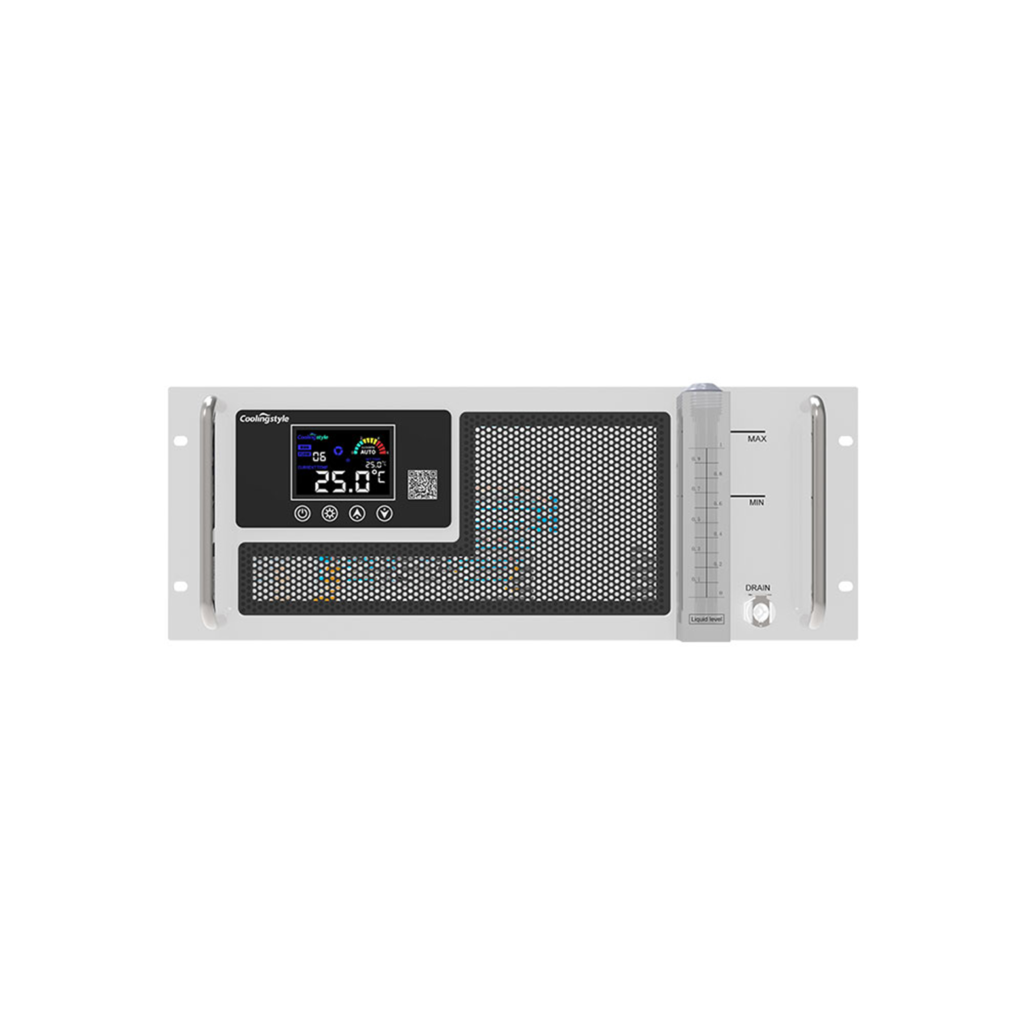

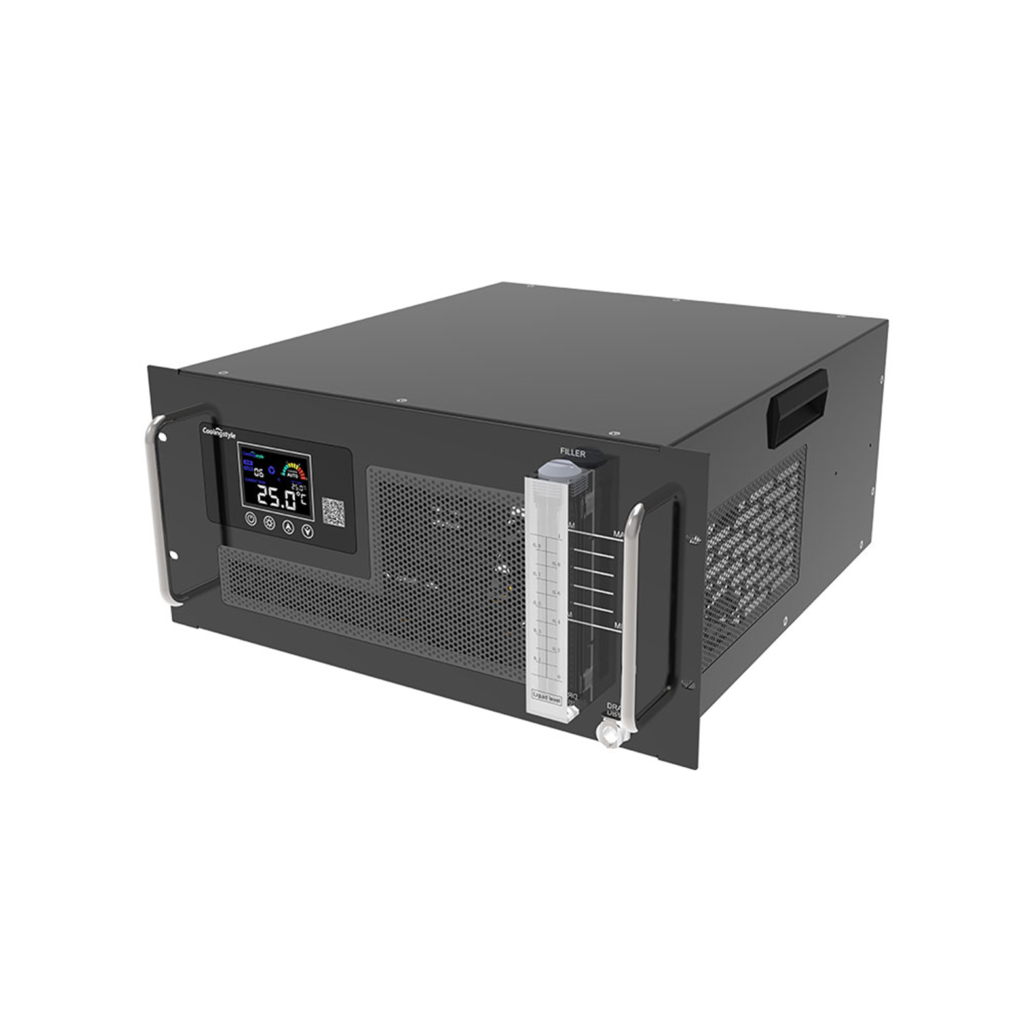
3. 1000W and 1200W cooling capacity chillers

Chiller temperature setting
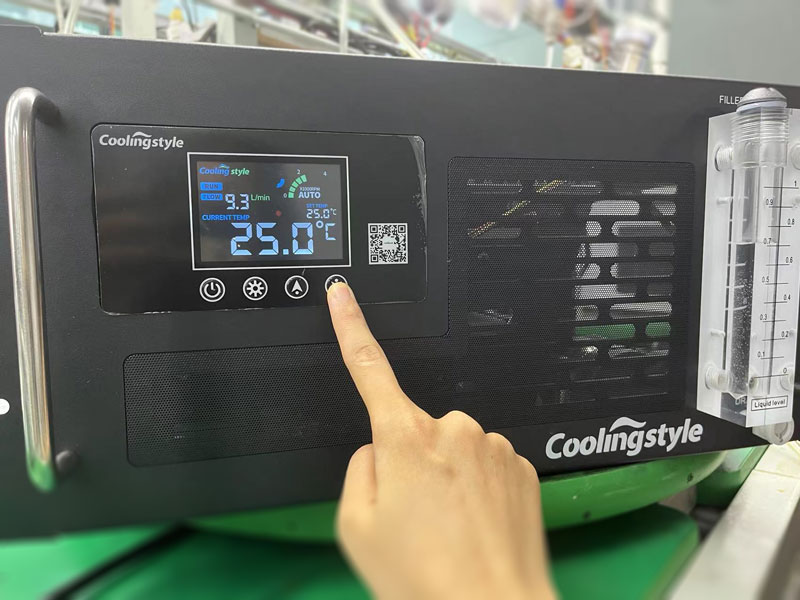

Considering the two factors of laser power and stability, Coolingstyle recommends setting the temperature of the CO2 RF laser coolant to 25±2℃. In hot summer, in order to avoid condensation, it can also be set at 28±2℃.
In winter, when conditions permit, we try to keep the chiller running continuously. At the same time, in order to save energy, it is recommended to adjust the temperature of low temperature and normal temperature water to 5 ~ 10℃, to ensure that the coolant is in a circulating state and the temperature is not lower than the freezing point.
Professional brand antifreeze can also be used if necessary (do not use ethanol instead, it may also cause damage)
For more information about the coolant choice, you may visit this blog for reference: